The shipping sector is facing increasing pressure to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions and improve its energy efficiency. Ship-aH2oy provides a solution: green hydrogen from LOHC combined with high-power solid oxide fuel cells to generate zero emission power onboard ships.
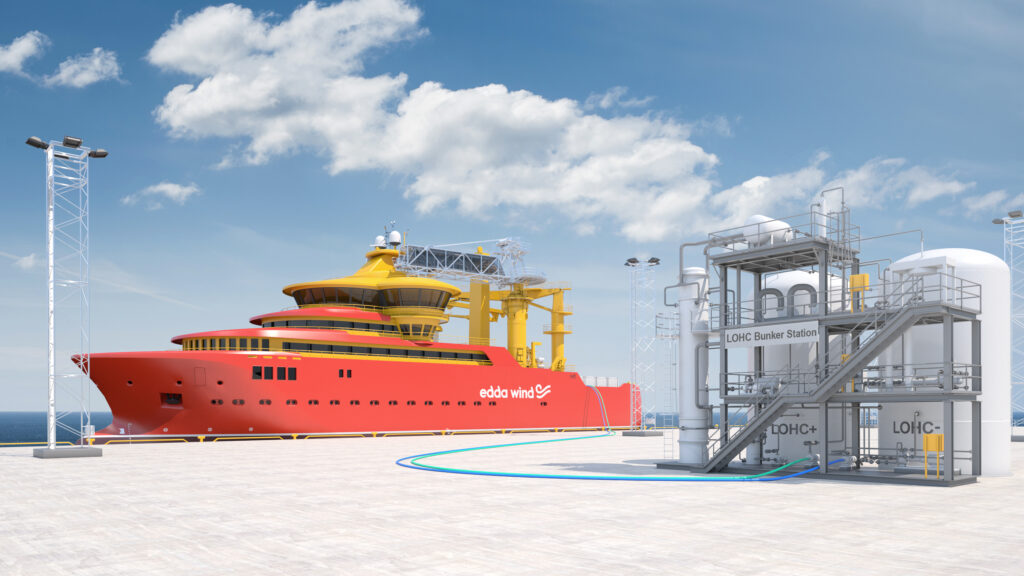

The goal of Ship-aH2oy is to introduce solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC) and liquid organic hydrogen carrier (LOHC) technology for marine use. This will result in a scalable and sustainable power and heat generation system on board ships with high energy efficiency.
The proposed solution will be demonstrated onboard an existing and available offshore wind vessel. A replication study will assess its potential for other vessel types.
EU has awarded the project €15 million in funding through the Horizon Europe program as part of its drive to decarbonize shipping.
Safe and sustainable fuel
LOHC adds a new way of handling hydrogen onboard ships. Instead of using compressed or liquid hydrogen, hydrogen is chemically bound to a carrier oil. This oil can be used to store and transport large amounts of hydrogen safely within existing fuel infrastructure.
The LOHC technology used in Ship-aH2oy also significantly increases the safety onboard as the carrier oil, Benzyltuolene, is non-explosive and hardly flammable.
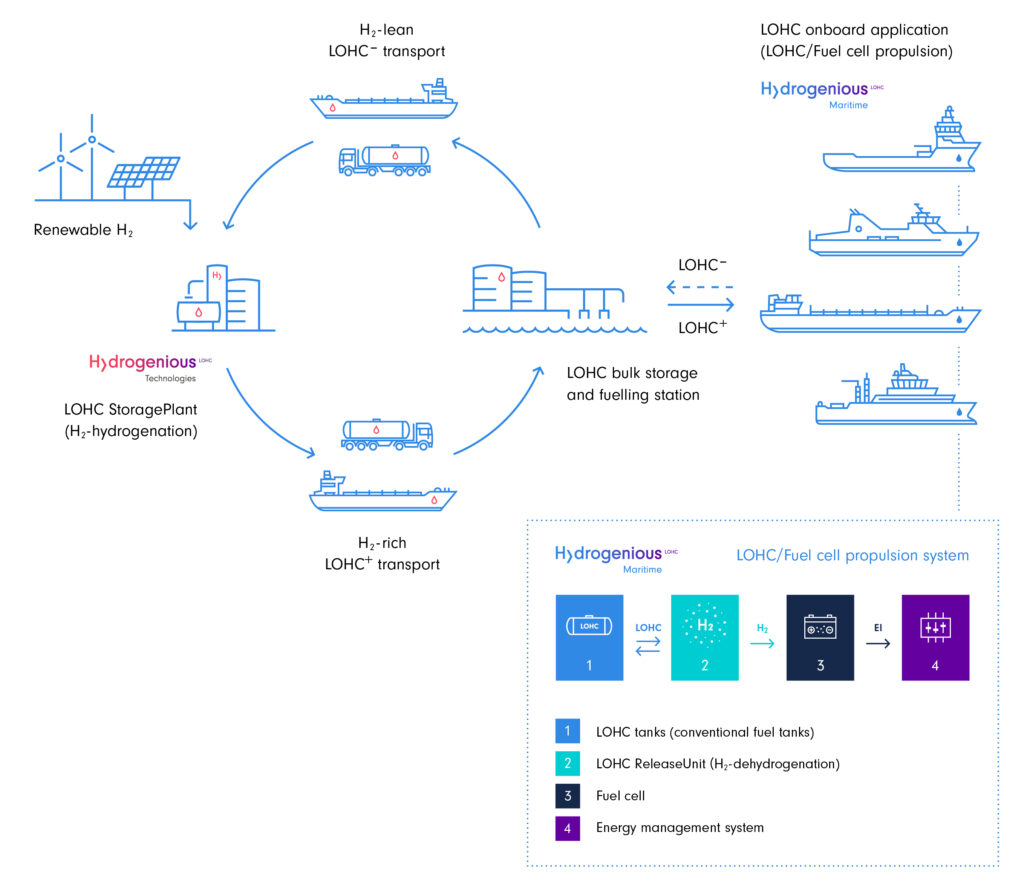
An efficient system
A hydrogen release unit onboard the ship releases the hydrogen from the LOHC to be used as fuel for the SOFC. The waste heat from the fuel cells will be recovered and used for the hydrogen release unit as well as the ship’s heating needs.
In this way, the system aims to achieve 85% overall energy efficiency, a significant improvement from conventional internal combustion engines.
A scalable solution
A 1 MW hydrogen power unit, consisting of a fuel cell and the hydrogen release unit, will be installed on a service operation vessel owned by Edda Wind, operated by Østensjø Rederi.
The demonstrator ship is part of Edda Wind’s fleet of C/SOVs for offshore wind operations. The vessels are all designed with spare room for the future installation of hydrogen power units up to 3 MW.
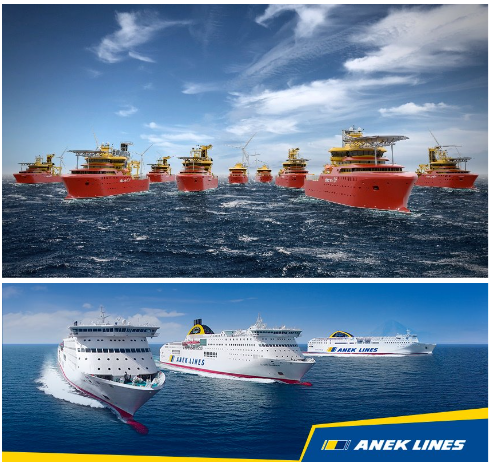

The project will also include a replication study for integrating the fuel cell on board a passenger ship operating on coastal waters. The implementation and demonstration will prove that the concept developed during Ship-aH2oy is scalable above the 3 MW level.
A strong consortium
The basis of Ship-aH2oy is the strong commitment of the wide range of industry partners to realize zero-emission shipping.

As the consortium covers the whole value chain from design offices and class society to shipbuilders, owners and operators, efficient dissemination and exploitation of the results will be a natural outcome of the project.
The consortium includes a total of 17 partners from 7 European countries.
More information?
See our frequently asked questions (FAQ) or get in touch!
